ARTICLE SUMMARY
Companies from different industries around the world have been using RPA (Robotic Process Automation) technologies in their processes to avoid waste and to become more efficient.

Companies from different industries around the world have been using RPA (Robotic Process Automation) technologies in their processes to avoid waste and to become more efficient. But when we talk about RPA we need to talk about Lean too, assuming that you want to extract the most out of an RPA system.
Even if you aren’t aware, RPA and Lean walk together to enhance productivity and better performance. We will show you how these two systems blend and why they are truly best friends. Moreover, we will demonstrate outcomes of the perfect integration between RPA and Lean through the VAREO model. You will soon understand why there is no RPA without Lean.
Starting Lean, Becoming RPA
The core principles of Lean are as follows:
- Identifying Value
- Value Stream Map
- Creating Flow
- Establishing a Pull System
- Continuous Improvement
These practices grant better process flow, allowing things to run smoothly and flawlessly. This way, the company can deliver more value while reducing waste, the greatest benefit and purpose of Lean. It is indispensable for successful businesses to be aligned with these principles. If you’re starting your Lean journey, we suggest more reading on the subject.
First of all, you have to understand the difference between Lean and RPA. With Lean concepts, such as A3, 3 M’s and the 7 Wastes, you will lay the groundwork for stronger RPA applications. In other words, gain efficiency. Once everything is working properly, the RPA software will step into the scene to automate operations as much as possible and to boost productivity.
RPA Easy and Done
RPA is not only emerging as a possibility for more productive processes, but also as an agent to revolutionize the way we work. This technology allows human workers to be discharged from manual, repetitive and futile tasks, replacing them with automatized systems, or robots, that follow predefined rules. Workers can then use their talents for more valuable efforts, such as problem-solving, strategy design and critical thinking.
RPA can be applied in numerous fields, such as sales, accountability, human resources, data management and much more. Check out some examples of usability:
- Data cleansing
- Forms processing
- Payroll processing
- Financial processes
- Shipping notifications
- Compliance reporting
- Call center operations
- Credit card applications
- System access and setup
- Customer order processing
- Customer complaints processing
- Transferring data from different systems
With so many applicable options, it is essential to make sure that the automatized processes flow properly, otherwise you will end up with a broken process multiplied a bunch of times (a Lean manager’s biggest nightmare). If a process is not designed to be efficient and impeccable, there’s no purpose in even considering applying RPA to it.
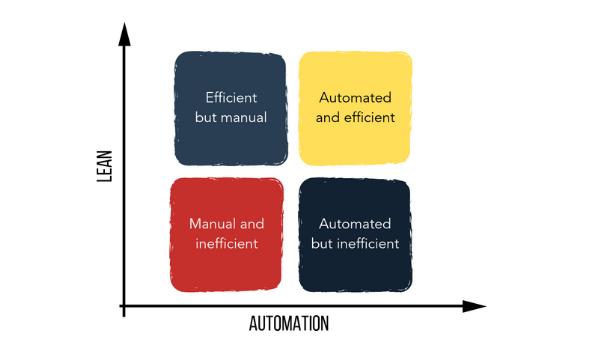
It is primordial to standardize a process, improve it, and lastly to automate it. Anyone who sees RPA as a possibility should understand the Lean principles to identify ineffective activities and eliminate them before starting to deploy automation. Remember that RPA is a journey, not just a project. You will have to work continuously on it!
Applying Lean Principles Before any RPA System
Although not mandatory, one of the first steps towards a successful RPA implementation is to perform an A3, which is a problem-solving framework in the shape of an A3 paper used to outline ideas, plans, and goals. You must have a clear vision of the current state of your process to identify its bottlenecks and work toward correcting them.
Consider the Whole Picture
Let’s suppose we’re talking about a company called Shinra Inc. that has very poorly designed HR processes and is considering implementing RPA. Currently, Shinra is struggling with slow, recurrent and vulnerable processes that demand manual care. The tasks involve recruitment processes, payroll systems, tax documents, time and records management.
The employees used sheets to track work time, something outdated and prone to errors. The recruitment process of onboarding was also overly manual since the HR team had to collect documents for verification, give access to new workers, deal with equipment requests, etc. Payrolls were a big issue considering they were done by hand with a higher chance of human mistake, not to mention exceptions such as bonuses and tax deductions.
These efforts drain valuable time from the employees, hours that could be better spent. Through the analyses provided by a full A3 overview, it was possible to identify the main root causes of bottlenecks the company faced such as the lack of integrated and digitized systems, hence demanding constant checking and manual work.

By establishing better control of flow in HR processes and mistake-proofing mechanisms (the so-called Poka-Yokes), the operations started to become leaner at Shinra Inc. To begin this sprint of progression towards the future state, other principles of Lean management are fundamental to better understand the whole picture, such as the 3 M’s.
Three M’s and the Seven Wastes
One of the top challenges companies face before implementing RPA is the frequent disarray the processes are found in. In order to deliver value with speed and quality, you have to have a steady and clear flow. To achieve a reliable flow, be aware of 3 M’s:
- Mura: unevenness
- Muri: overburden
- Muda: waste
When an uneven process is not reduced to zero, it invariably leads to waste. Waste, as we all Lean practitioners know, is our biggest enemy. The elimination of waste is essential in any process before applying RPA on it in order to deliver more value with fewer resources. Check out the 7 Wastes you should avoid at all costs:
- Motion
- Defects
- Waiting
- Inventory
- Transportation
- Overproduction
- Overprocessing
We can easily identify some of the 7 Wastes that were major bottlenecks in the HR processes at Shinra Inc. Check below:
- Motion: constantly walking around the office to deliver documents
- Defects: issues that emerged on payrolls processes done by hand
- Waiting: newly hired employees that had to wait for their requests to be resolved
These things can be improved by Lean techniques and boosted by RPA systems. For example, the elimination of paper usage in the office in favor of more digitized documents, a software for managing internal processes, bots that can answer the employee’s doubts, help them get access to tools, and help them schedule holiday requests and calculate payrolls.

RPA is the digital workforce of the office, combining artificial intelligence, machine learning, and robotic processes automation. The organization’s employees will be assigned to do better and more valuable tasks while you don’t have to worry about the basic stuff. Once everything is leaner, all human and robotic workers will benefit.
VAREO: the Consequence of it All
We’re in the final step of the desired state! VAREO is the definition of successful Lean + RPA implementations in any business. Through the VAREO model, you will increase productivity, mitigate operations risks, reduce operational costs and standardize your processes.
Keep in mind that robotization won’t save a badly designed process. That’s why it is crucial that your RPA journey includes some process modeling efforts. The best way to do that is by applying the Lean concepts to it. That means:
- Identifying and getting rid of all the waste and bottlenecks in your processes
- Making sure every phase of the processes is adding value
- Never stop improving every step of the way
This integration will help you achieve the VAREO model:
- Visibility: visualization of your whole process clearly so you can detect where value is created and where waste is generated.
- Automation: identification of which steps can be automated to perform specific tasks faster and more efficiently.
- Robotization: evaluation of how robots can help you by performing manual work that otherwise would be performed by humans.
- Exception: establishment of flow, which allows humans to manage exceptions and specific situations that may appear.
- Optimization: continuous improvement of your processes in order to have even better results in the future.
Benefits of Lean + RPA
Among the key benefits you’ll find in Lean + RPA integrated systems, the reduction of waste is one of the greatest. The company will eliminate waste in different ways, such as time, effort, and resources. Quality growth is another enormous gain considering you will be able to see your processes more clearly and check what adds value and what doesn’t.

As a consequence, the ROI will be maximized by smoother processes that perform better and generate faster results. Also, with the elimination of bottlenecks spawned by better process flow, employees are freed to use their talents for more valuable tasks.
When Lean and RPA work together, you can expect to obtain the ultimate operational excellence. But remember: become Lean before applying the tools of RPA. An ideal RPA system has to be Lean for it to offer the best possible results for your business.
Isn’t that what any manager wants?






