ARTICLE SUMMARY
Guide to managing your purchase order (PO).

Purchase order processes play a critical role in making your business succeed. Without an efficient and accurate process for managing POs, time and resources are wasted and unnecessary mistakes become common.
One challenge businesses in every sector face is the need to create a consistent, reliable process for generating, approving, and tracking purchase orders. Managers are often looking for ways to add accountability and standardization to their PO workflows, in order to gain control of (and insight into) their purchasing decisions.
If this sounds familiar, then this article is for you. Below, we’ll explore the purchase order process from beginning to end by defining the term, breaking it down into its basic components, and providing some best practices for POs, regardless of the size or industry of your business.
Build better workflows with the Citizen Developer’s Guide to Workflow Optimization
What is a purchase order?
A purchase order is a type of legal document that buyers send to sellers to register the sale of products and services.
Purchase order vs. Purchase requisition
The distinction between a purchase order and a purchase requisition lies in their roles within the procurement process.
A purchase requisition is a formal request submitted by an internal department or employee to the procurement team. It outlines the need for specific goods or services, including details like item descriptions, quantities, and justifications. A purchase requisition initiates the procurement process, signaling to the procurement team that a purchase is required to fulfill operational needs.
On the other hand, a purchase order is a formal document generated by the procurement team in response to an approved purchase requisition. The PO includes comprehensive details about the purchase, such as item specifications, quantities, prices, delivery dates, terms, and supplier information. Once issued, the purchase order serves as a legally binding agreement between the buyer and the supplier, outlining the terms under which the goods or services will be provided.
In summary, a purchase requisition is a request for procurement, initiated by internal departments, while a purchase order is the official document issued by the procurement team to a supplier, confirming the specifics of the purchase and establishing contractual terms.
Purchase order vs. Invoice
The difference between a purchase order and an invoice lies in their purpose and timing within the procurement process.
An invoice is generated by the supplier and sent to the buyer after the goods or services have been delivered. It is a request for payment, detailing the actual costs of the items or services provided, any applicable taxes, and payment terms. The invoice serves as a billing document that formalizes the financial aspect of the transaction.
In essence, a purchase order is a proactive document that initiates the purchasing process, while an invoice is a reactive document that concludes the transaction by requesting payment for the delivered goods or services.
What is a purchase order process?
Purchase orders (PO) help businesses understand and account for all the goods or services that they have requested. Managers can use POs to keep tabs on additional, relevant information such as quantity, delivery instructions, cost, terms, and date required.
The purchase order process consists of all the steps businesses take to create, approve, validate, manage, and track POs, from the moment a need is identified up to the point of delivery or sale.
7 steps of the purchase order process
While the PO process for your company may be unique in some ways, there are 7 elements of the workflow that are common to most, if not all, purchase order processes. Here are the most common purchase order process steps:
- Order creation
- Approval
- Dispatch
- Binding contract
- Goods delivery
- Three-way match
- Closure
1. Order creation
The first step in the PO process is to create a purchase request. At this point, you’ll need to know what is being purchased, the priority level of the requisition, your budget, when the product or service is needed, who needs to approve the order, and the suppliers.
2. Approval
After the order has been created, the next step in the process is to get approval of the purchase requisition. In some cases, this approval may be verbal or sent as an email. In other companies, more formal actions, such as completing paperwork, may be required.
The level of approvals depends on the purchase amount, company policies or guidelines, and the requirements of the supplier. Approvals may also require verification of budget or documentation, such as product specs or detailed statements of work (SOW). After approval, the requisition turns into a PO.
3. Dispatch
After the requisition is approved, the PO is sent to the selected vendors. The vendors then submit bids based on the POs. The bids are approved based on price, quality, support, service, schedule, and other factors relevant to your business.
4. Binding contract
After the bid is accepted, the company and the vendor must agree to a contract. The contract typically includes terms and conditions relevant to the purchase, such as what support comes with the item being purchased or how to handle any disputes.
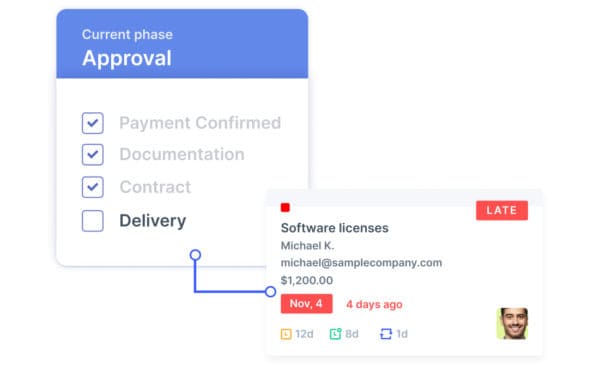
5. Goods delivery
The supplier will then produce and deliver the items being purchased based on the outlined schedule and shipping requirements. Your company will verify quality and match the goods received against the expected goods. From there, you can notify the supplier if the goods don’t meet your requirements. Typically, the supplier will send the purchasing company an invoice that outlines the price and payment terms.
6. Three-way match
After the goods received are approved, the purchasing company will then match the purchase order with the PO and invoice from the supplier. Companies should check to ensure that all charges are accurate.
7. Closure
After the three-way match is approved, the purchase order is closed out.
Main types of purchase order
There are several types of POs used in procurement processes. The main ones are these:
- Standard purchase order: The most common type. It specifies the details of the goods or services being purchased, including quantities, prices, and terms.
- Blanket purchase order: Used for repetitive purchases, it establishes an agreement with a supplier for a specific period, often with predetermined pricing and terms.
- Planned purchase order: Also known as a planned release order, it’s a preliminary order indicating an organization’s intent to purchase specific items, but details like quantities and delivery dates are confirmed later.
- Emergency purchase order: Used for urgent situations, it allows for expedited procurement without adhering to regular approval processes.
- Single-source purchase order: Issued to a specific supplier, indicating the intention to procure goods or services from them exclusively.
- Direct purchase order: Used when items are directly purchased from suppliers without intermediary parties.
- Indirect purchase order: For non-production-related items, such as office supplies, maintenance services, or equipment, which support the organization’s operations.
What is the format of a standard PO?
The format may vary based on organizational preferences, industry norms, and the complexity of the purchase. However, it typically includes key information required for the transaction, such as:
- Header information: This includes the buyer’s and supplier’s names, addresses, contact details, and the date of issuance.
- Purchase order number: A unique identifier assigned to the PO for tracking and reference purposes.
- Order details: This section specifies the items or services being purchased, including descriptions, quantities, unit prices, and total amounts.
- Delivery information: The desired delivery date, shipping address, and any special instructions related to the delivery.
- Payment terms: The agreed-upon terms for payment, including due dates, currency, and any applicable discounts or penalties.
- Billing information: If different from the shipping address, the billing address where the supplier should send the invoice.
- Additional terms and conditions: Any specific terms, conditions, or legal requirements that apply to the transaction.
- Authorized signatures: Space for the authorized personnel from both the buyer and supplier to sign, indicating their agreement to the terms.
- Attachments: Supporting documents, such as product specifications, drawings, or contracts, that provide additional context to the order.
Why is it important to implement a purchase order process?
A consistent, repeatable PO process provides a range of benefits, including enhanced control, visibility, and efficiency.
Budgeting
Consistent PO processes help your finance department accurately account for all relevant purchase expenses and maintain forecasts and budgets.
Order management
An established PO process allows you to manage many orders at once and provides visibility into related activities, such as shipping and receiving, inventory control, and production planning. In addition, a healthy purchase order process should allow for transparency at every touchpoint along the way.
Financial accountability
A robust PO process will create a paper trail for cash flows and add accountability for the cost of goods along the way. Banks, auditors, and legal departments will see this as an asset for your company.
Dispute resolution
Creating a legal contract between your company and your suppliers during the PO process helps define responsibilities and resolve disputes. Terms and conditions are clearly stated, and details such as warranties, guarantees, or other policies are set down in black and white.
Best practices for optimizing your PO process
Businesses evolve, and their processes need to be retooled from time to time to remain efficient and accurate. PO processes are no exception.
The immediate risks of not maintaining your PO process include errors, waste, overspending, under budgeting, and, ultimately, high burn rates. That’s to say nothing of the stress and disorder an outdated PO process can cause you or your team. In the long term, an inefficient or inaccurate purchase order process can also cause problems in your relationships with suppliers and your ability to acquire goods or services on pace with your company’s needs.
Managers preparing to improve their PO processes should consider the following best practices:
- Review and analyze your current purchase order process
- Establish goal-oriented results
- Create written guidelines accessible to everyone in the PO process
- Develop a list of preferred vendors
- Create budget allowances and expense groups
- Assign an internal stakeholder to manage the process
- Leverage technology
Review and analyze your current purchase order process
Every process in every business should be continuously reviewed and analyzed for areas of improvement. Make sure to map each step out, identify and resolve any bottlenecks, identify the number of approvals required in the process, and account for the different factors that might be impacting your budgeting process. You should also review key stakeholders in your process — internal players and long-term vendors — and how technology can be integrated to help orchestrate this process.
Establish goal-oriented results
Outline and detail goals surrounding your purchase order process. Consider metrics revolving around speed of deliveries, reliable vendors, or reduced spending.
Create written guidelines accessible to everyone in the PO process
A written process is a great way to communicate best practices and standardized procedures to an entire company. These rules and policies should include the necessary information required for each step of the process, number of approvals needed, and who the internal reviewers are.
Develop a list of preferred vendors
This list will help your team quickly pick from a go-to list of vendors your company has built longstanding and trusted relationships with and negotiate the best deals.
Create budget allowances and expense groups
These budgetary restrictions help streamline the process by automatically implementing purchase guidelines. For example, if a company has a monthly budget of $1000 allocated to office supplies, the finance team knows how much they have to spend for necessary resources.
Assign an internal stakeholder to manage the process
Having someone oversee this process helps improve company-wide adoption and provides a point of contact to answer questions that might come up when implementing a new procedure.
Leverage technology
Integrating a purchase management system into your company’s PO process is an easy way to standardize procedures and replace repetition with automation.
Benefits of automating the purchase order process
PO tracking can be managed through emails and spreadsheets or by using dedicated software. Using software to manage and simplify your PO process is an easy way to save time, money, and stress. Key benefits of automating your purchase order process include:
- Reduced repetition: A PO management tool can free up time by automating some tasks, allowing you to focus on other priorities.
- Increased transparency: Creating a standardized PO process and defining information requirements, such as quantity requested or approval signatures, will add accountability and clarity to your purchase orders.
- More control: Purchase management software helps you control expenses and improve budgeting, as well as provide a complete audit trail. It also lets financial stakeholders easily view or share information.
- Centralized and visualized data: Data is consolidated into a single source of truth to make it faster and easier to manage POs. Since data is centralized, you’ll also have the option to run reports and create visualizations to help you keep control of many purchase orders at once.
FAQ about purchase order process
What is the purpose of a PO?
The purpose of a purchase order is to formalize an agreement between a buyer and a supplier for the procurement of goods or services. It outlines the specifics of the transaction, including item details, quantities, prices, and terms, providing a reference for both parties to ensure accurate order fulfillment, delivery, and payment.
What is a standard PO used for?
A standard PO is a common tool in procurement to ensure clarity and alignment between both parties throughout the purchasing process.
What is the PO approval process?
The PO approval process begins with the submission of a purchase requisition for evaluation. Upon approval, a purchase order is created, outlining the purchase details and sent to the supplier. This process might involve various levels of approval to ensure compliance with budgets, specifications, and internal policies before finalizing the procurement.
Who approves a purchase order?
The approval of a PO involves relevant stakeholders within an organization. Depending on the organization’s structure and policies, these stakeholders could include department managers, budget holders, procurement officers, and higher-level executives.
How do I process a PO payment?
Processing a purchase order payment involves several steps. First, verify the received goods or services match the PO details. Then, reconcile the supplier’s invoice with the PO and any supporting documentation. Obtain necessary approvals for payment. Input payment details into the financial system. Finally, initiate the payment as per agreed terms, ensuring accuracy and compliance with internal processes.
Do you receive or bill a PO first?
In the purchase order process, the sequence usually involves receiving the goods or services from the supplier first. After this, the supplier sends you an invoice for the delivered items. You then compare the invoice details with the purchase order to ensure accuracy before proceeding with payment.
How long does it take for a PO to be paid?
The time it takes for a purchase order (PO) to be paid varies based on factors such as the payment terms negotiated between the buyer and the supplier, the internal processes of the buying organization, and any potential delays or discrepancies that might arise during the invoicing and reconciliation stages.
Payment terms specified in the PO, such as “Net 30” or “Net 60,” indicate the number of days the buyer has to make the payment from the date of invoice submission. However, actual payment timelines can fluctuate.
FAQ – Take control of your PO process with AI Agents
What are AI Agents?
AI Agents are systems powered by artificial intelligence that can automate tasks, interact with users, and make decisions based on data, optimizing processes across various business areas.
Do AI Agents replace human workers?
No. They support decision-making, eliminate repetitive work, and enhance efficiency—but human judgment remains critical.
Do I need a tech team to use AI agents?
Not necessarily. Many platforms offer no-code interfaces and technical support, so business teams can set up workflows without writing code.
What should I consider before implementing AI agents in my company?
- Scalable personalization: AI agents that integrate with BPM systems
AI agents can analyze large datasets and provide personalized interactions. Integrated with Business Process Management, this personalization can be applied consistently across different channels. - Intelligent automation: AI agents combined with BPA
By combining AI agents with Business Process Automation, companies can handle repetitive tasks and even complex analysis—like document interpretation and decision-making—automatically. This frees teams to focus on customer relationships.
And if you want to learn how AI agents can bring exponential efficiency to your procurement department, click the button below and schedule a demo with Pipefy’s solution.






